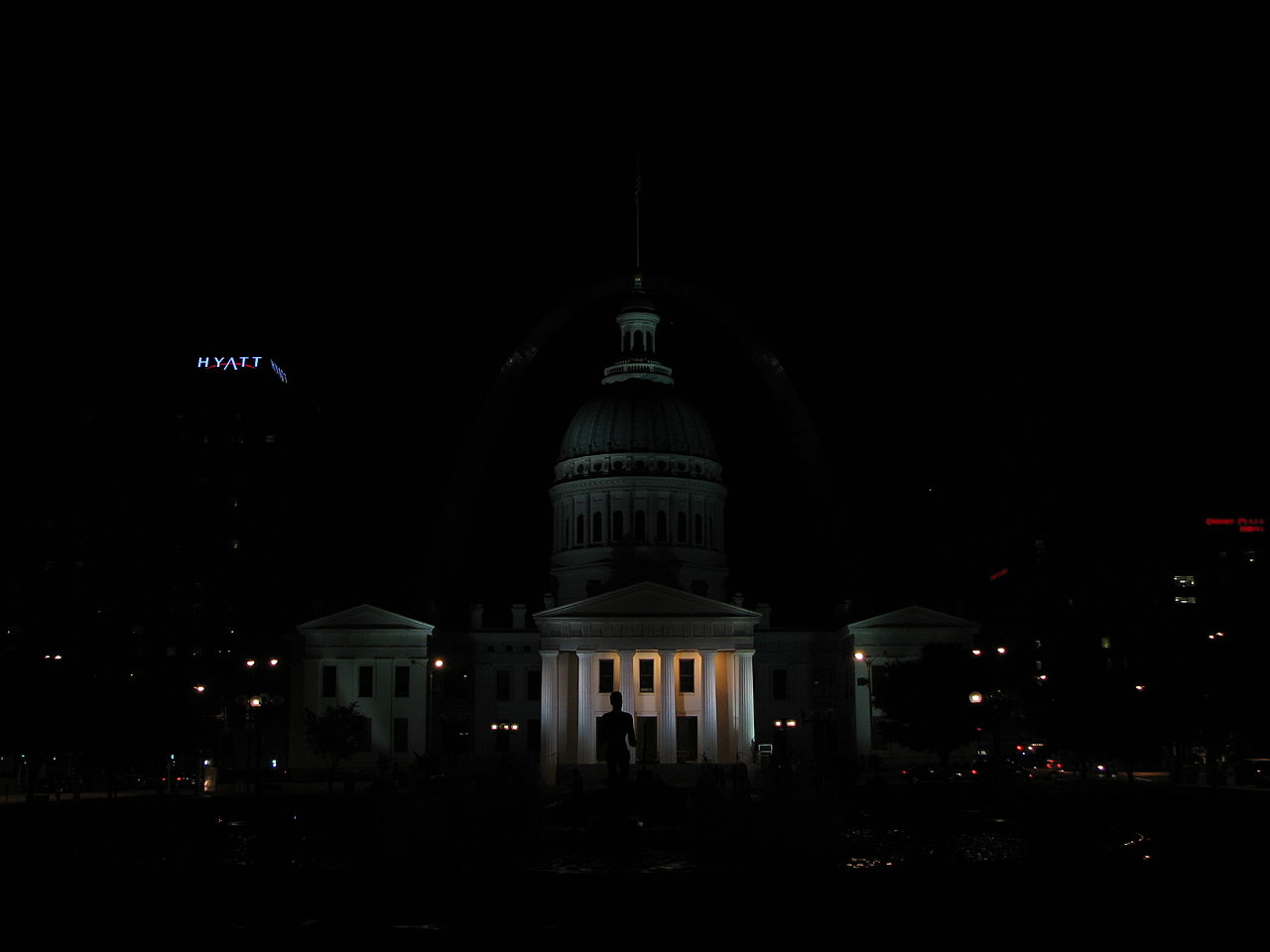

1/25s
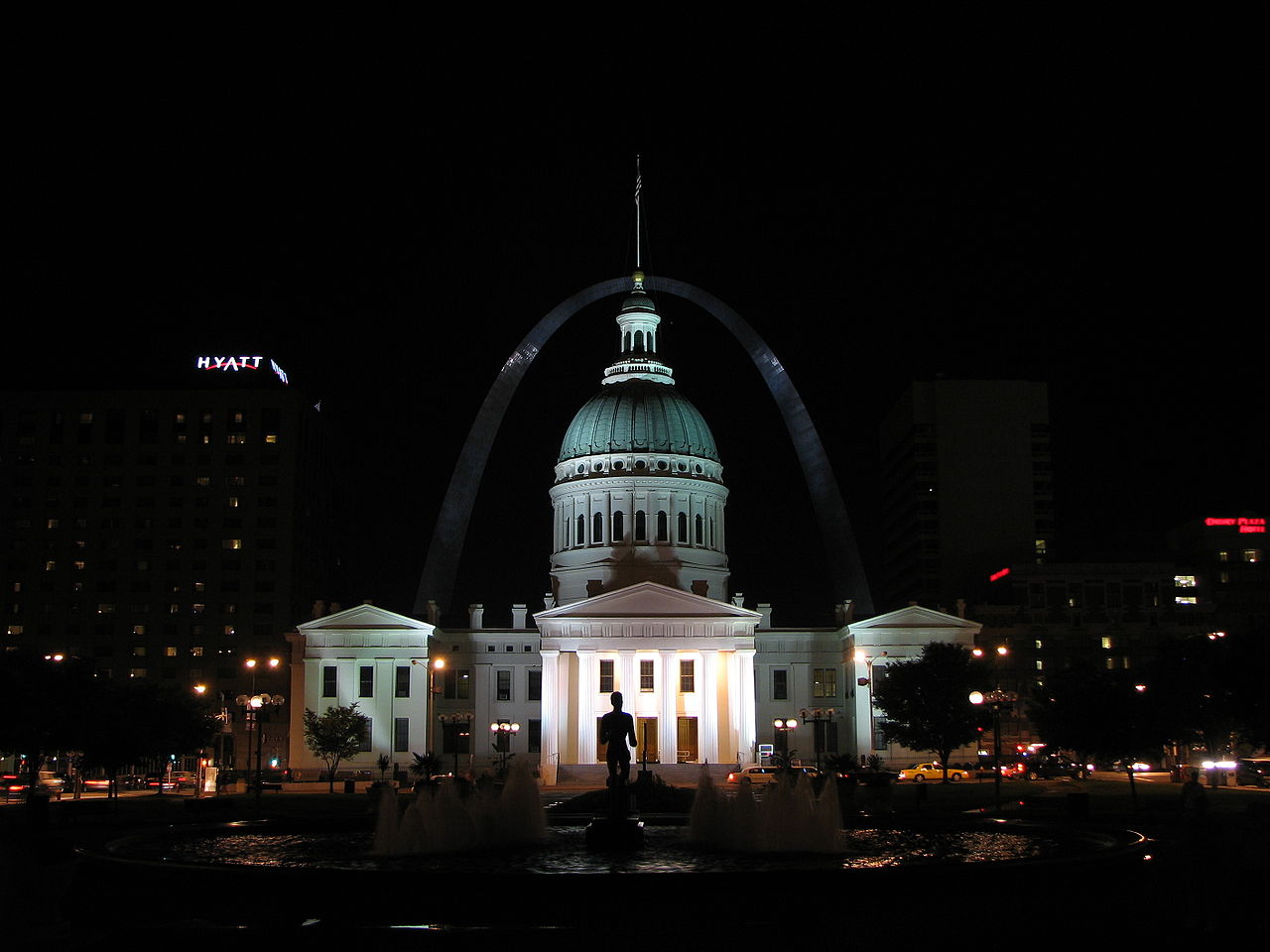

1/4s
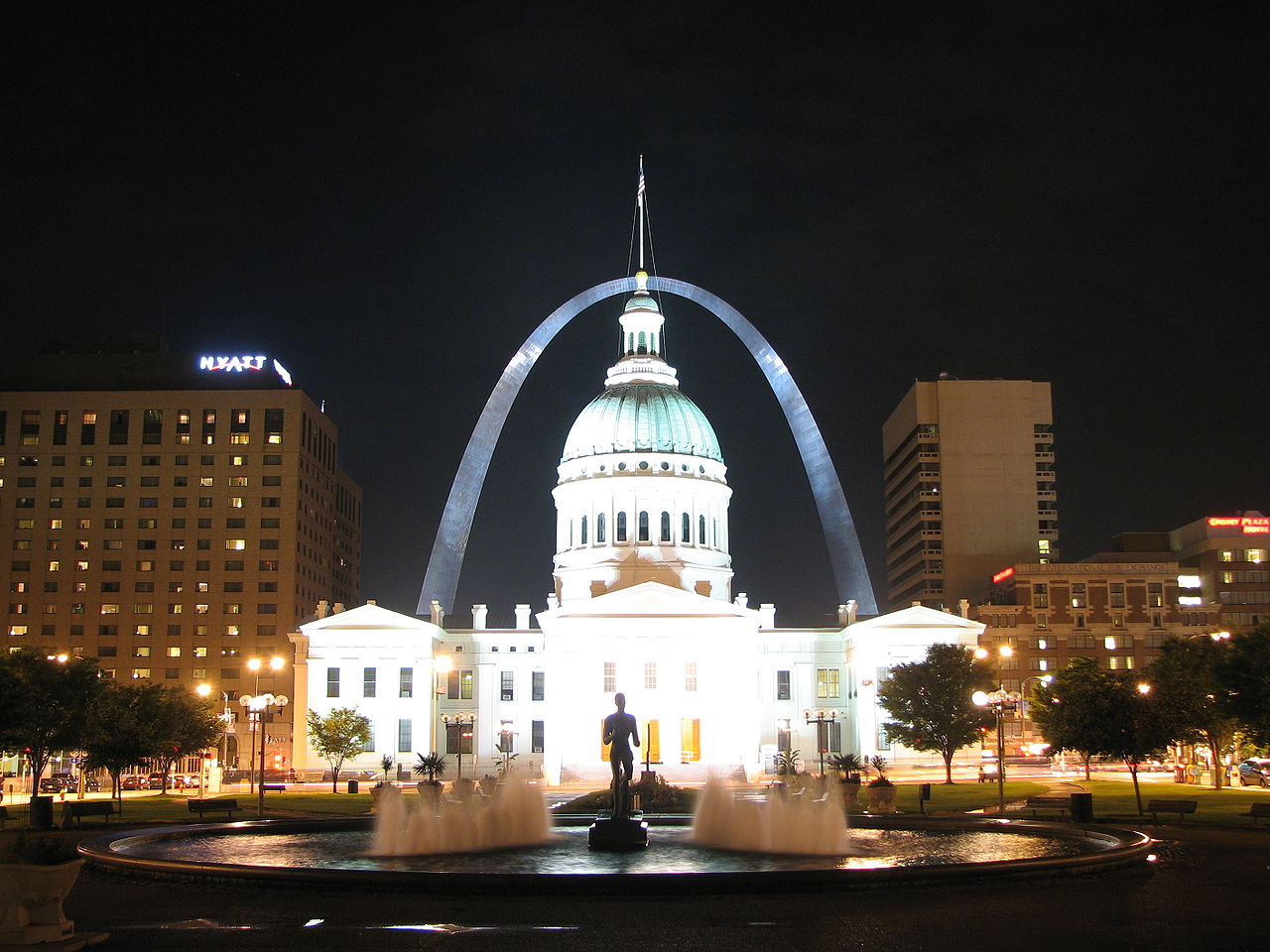

3s
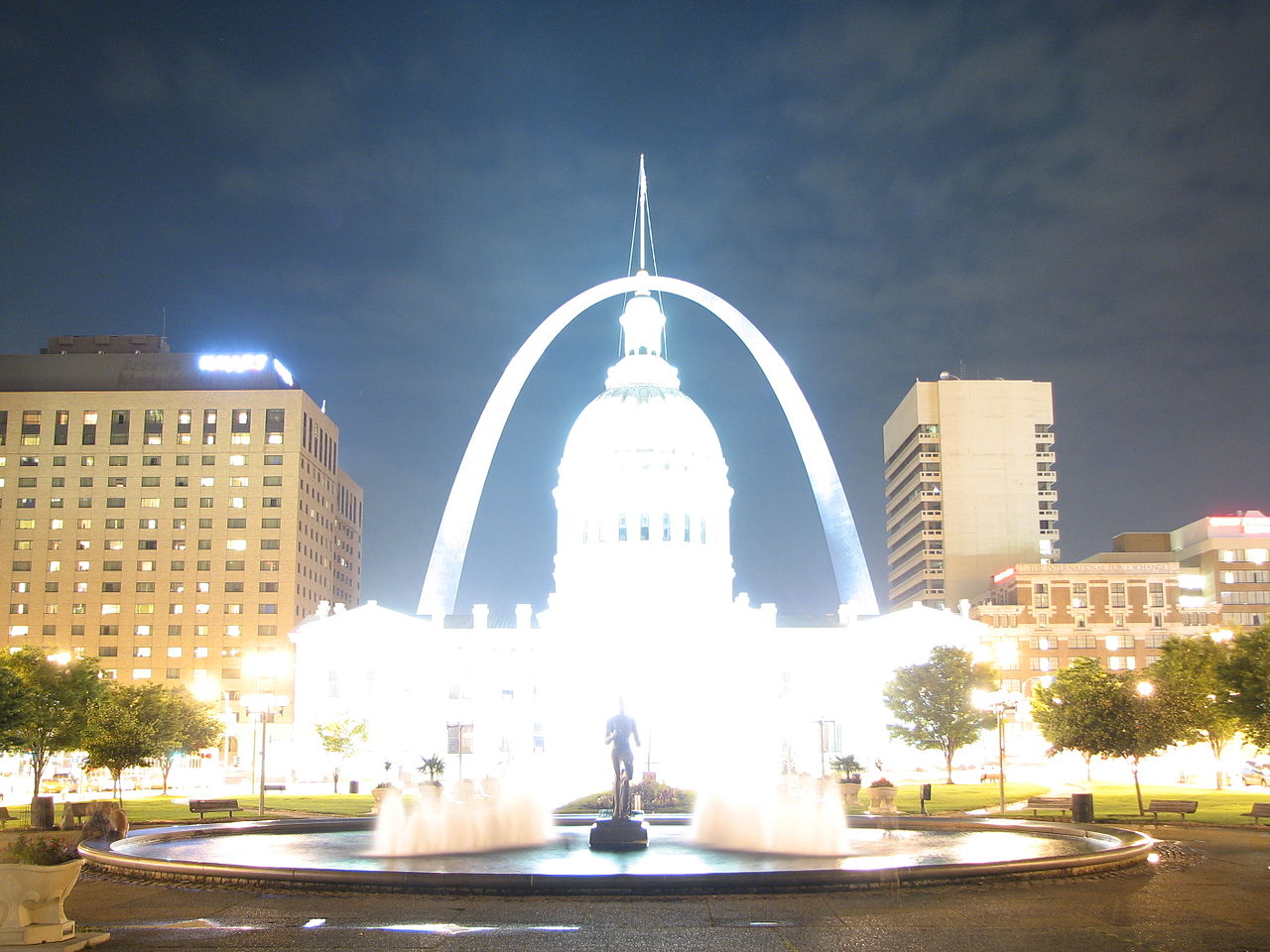

17s
Modern cameras are unable to capture the full dynamic range of real-world scenarios. Combining information from multiple exposures of the same scene can allow us to capture high dynamic range photos.
HDR radiance maps can be created from several LDR exposures. This is because a pixel at each image is a function of an unkown scene radiance, integrated over the exposure time. Therefore, we can solve for the radiance by making some base assumptions of the function as well as the natural log of it. The radiance map shows the intensity values at different points in the scene, with lighter areas being more intense, and darker areas being less.

1/25s

1/4s

3s

17s
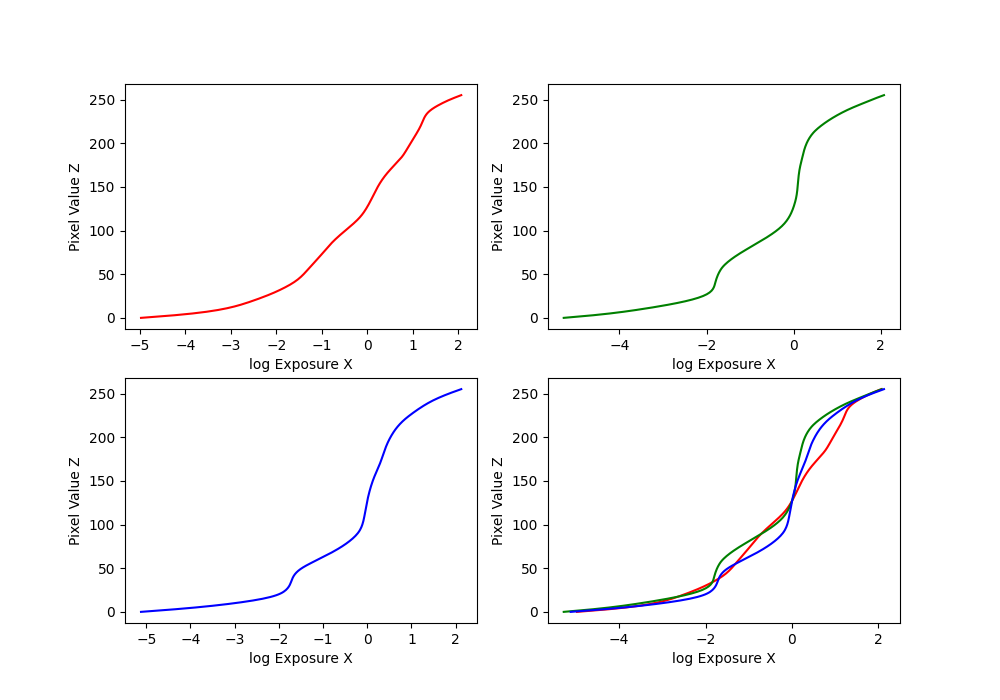
Pixel vs Log Exposure
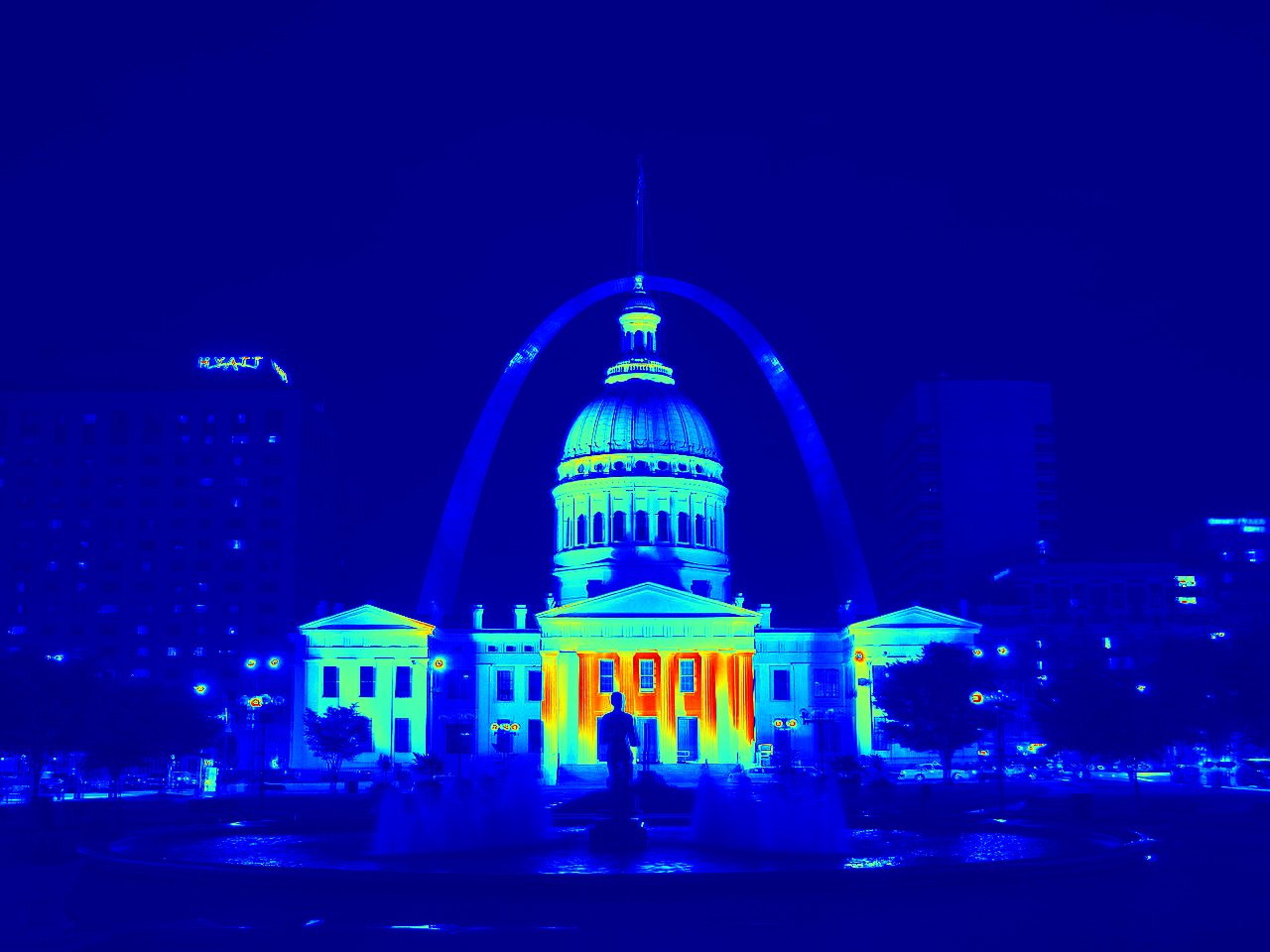

HDR Radiance Map Mean

HDR Radiance Map
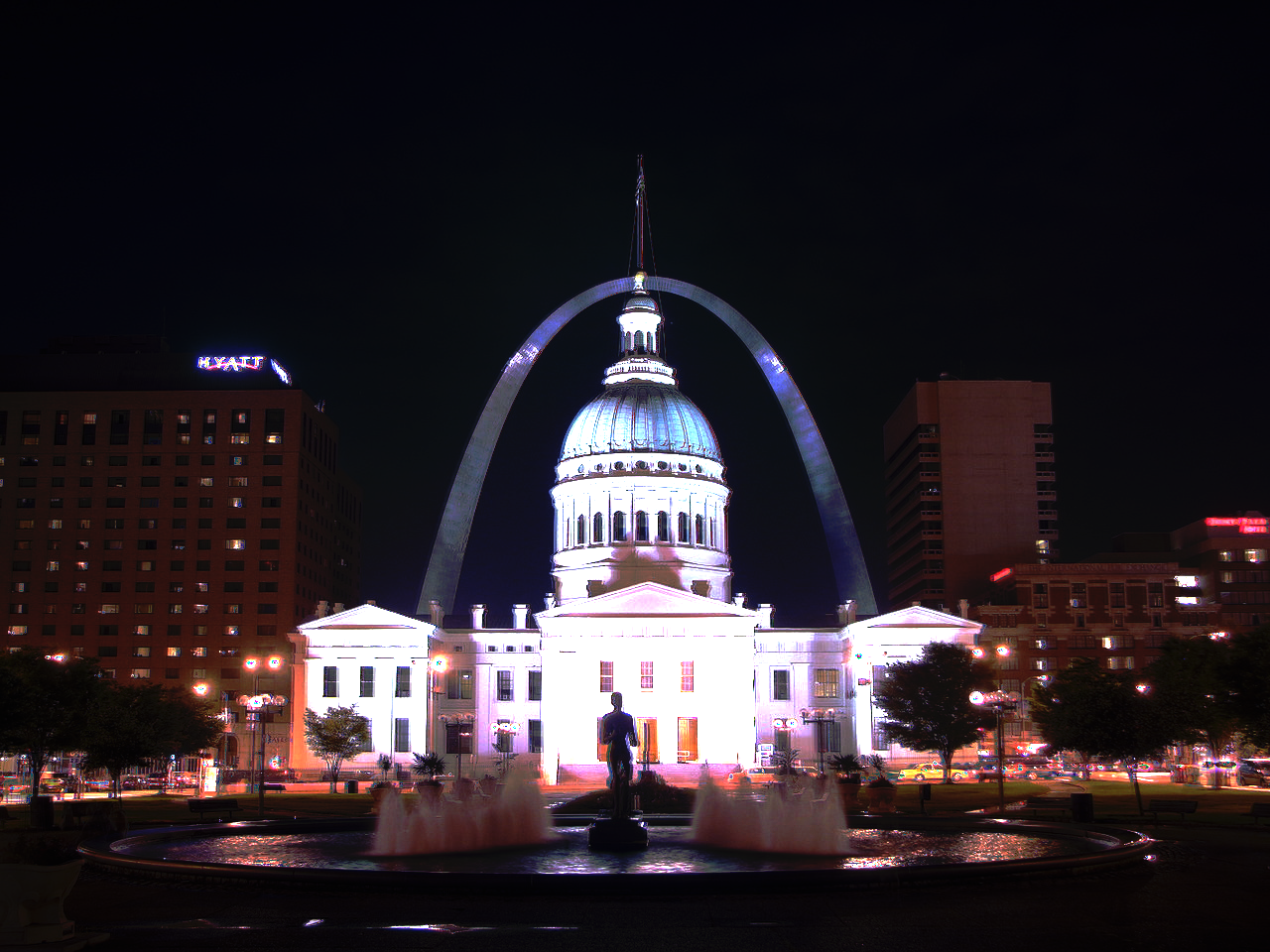
Global tone mapping can be done to show off the image, as the values are not within the typical 0-1 or 0-255 range. Thus, L / (L + 1) provides a global tone mapping to view the image, however, it does a poor job of stretching the full dynamic range. Thus, a simplified Durand 2002 tone mapping is done to locally tone map the image and show the full dynamic range. The durand tone mapping incorporates calculating the intensity, chrominance channels, bilateral filtering, scaling and reconstructing, as well as gamma compression.

Bilateral Large Scale Structure

Details
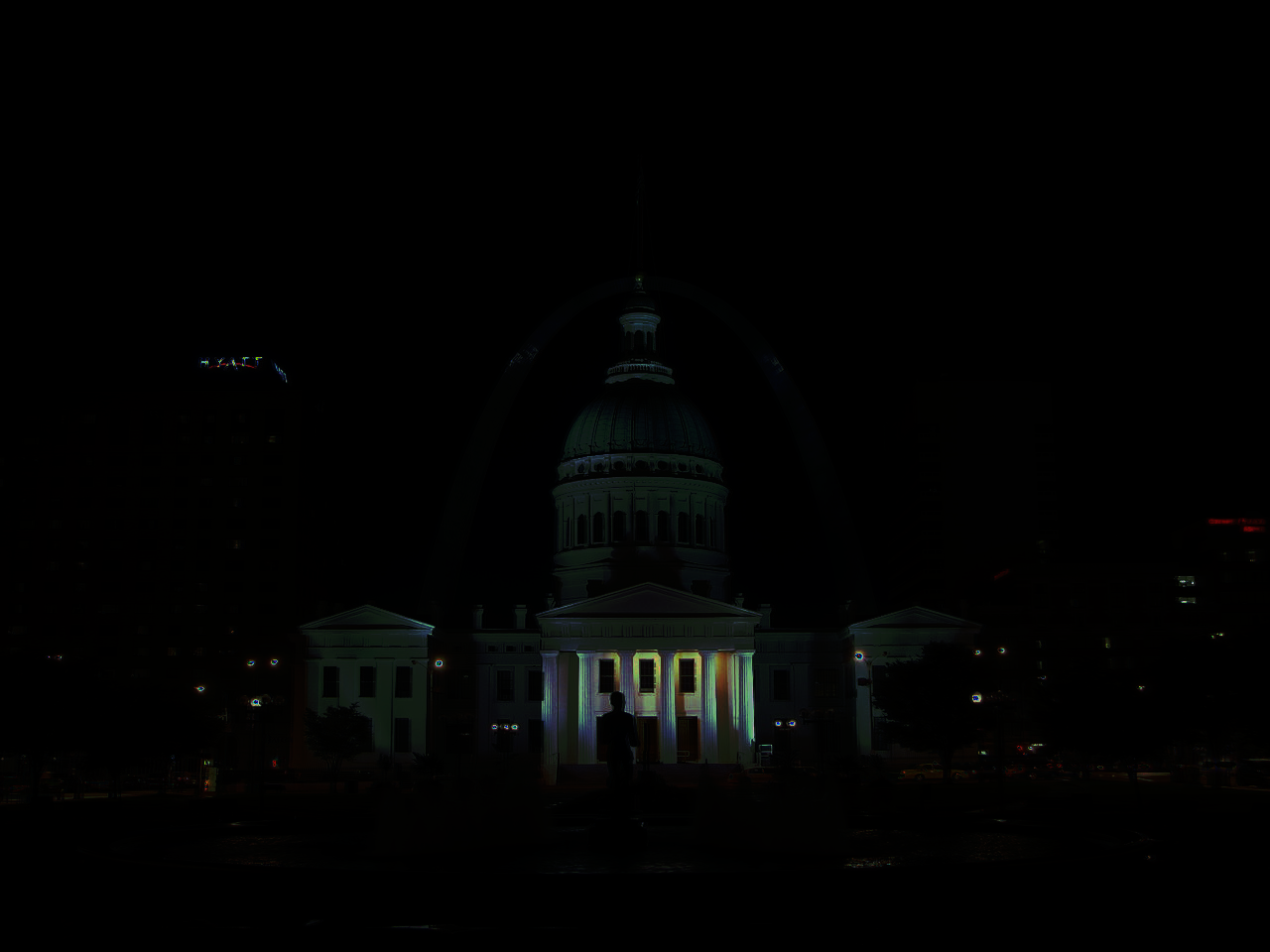

Global Scale
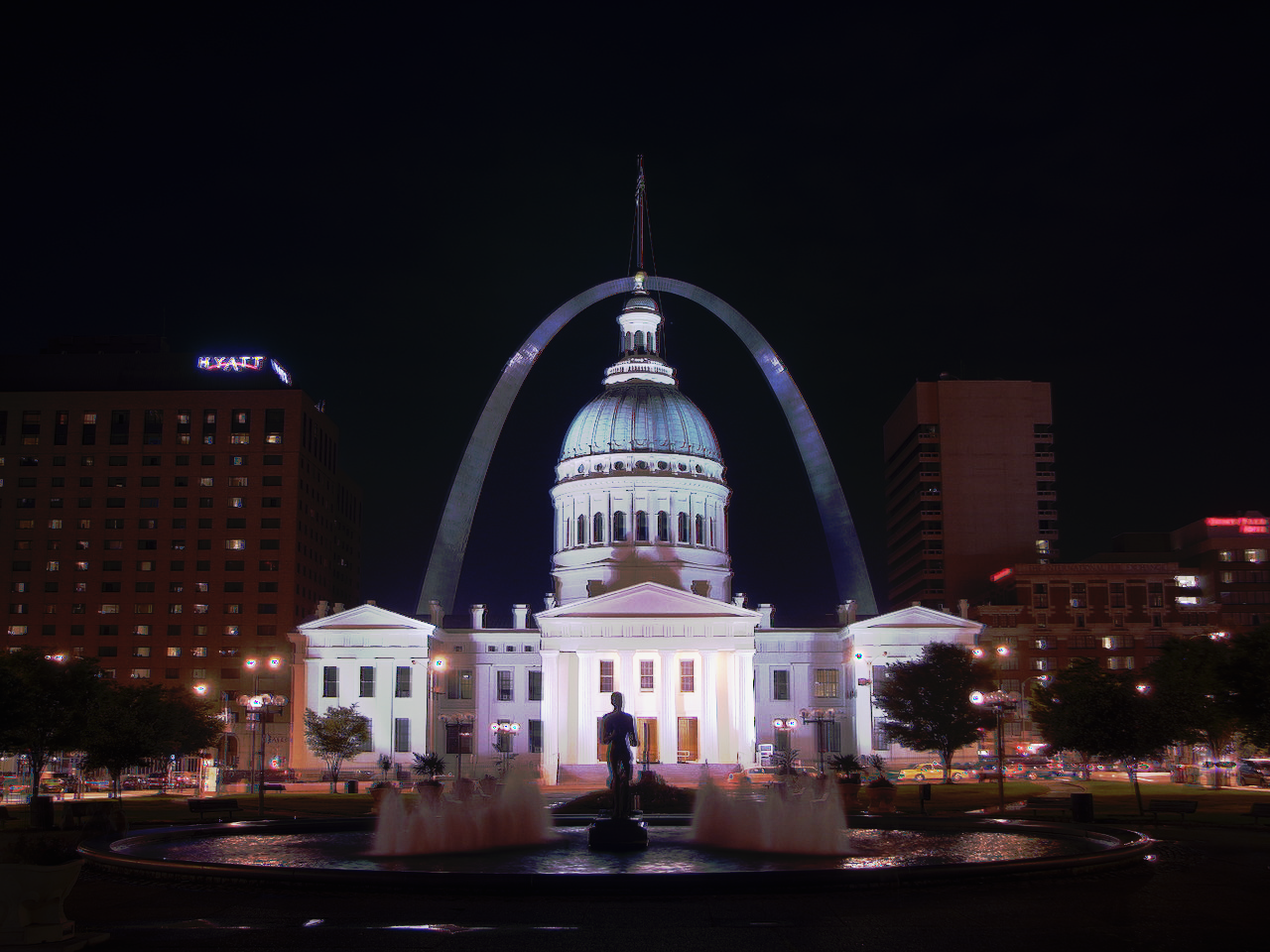

Global Simple
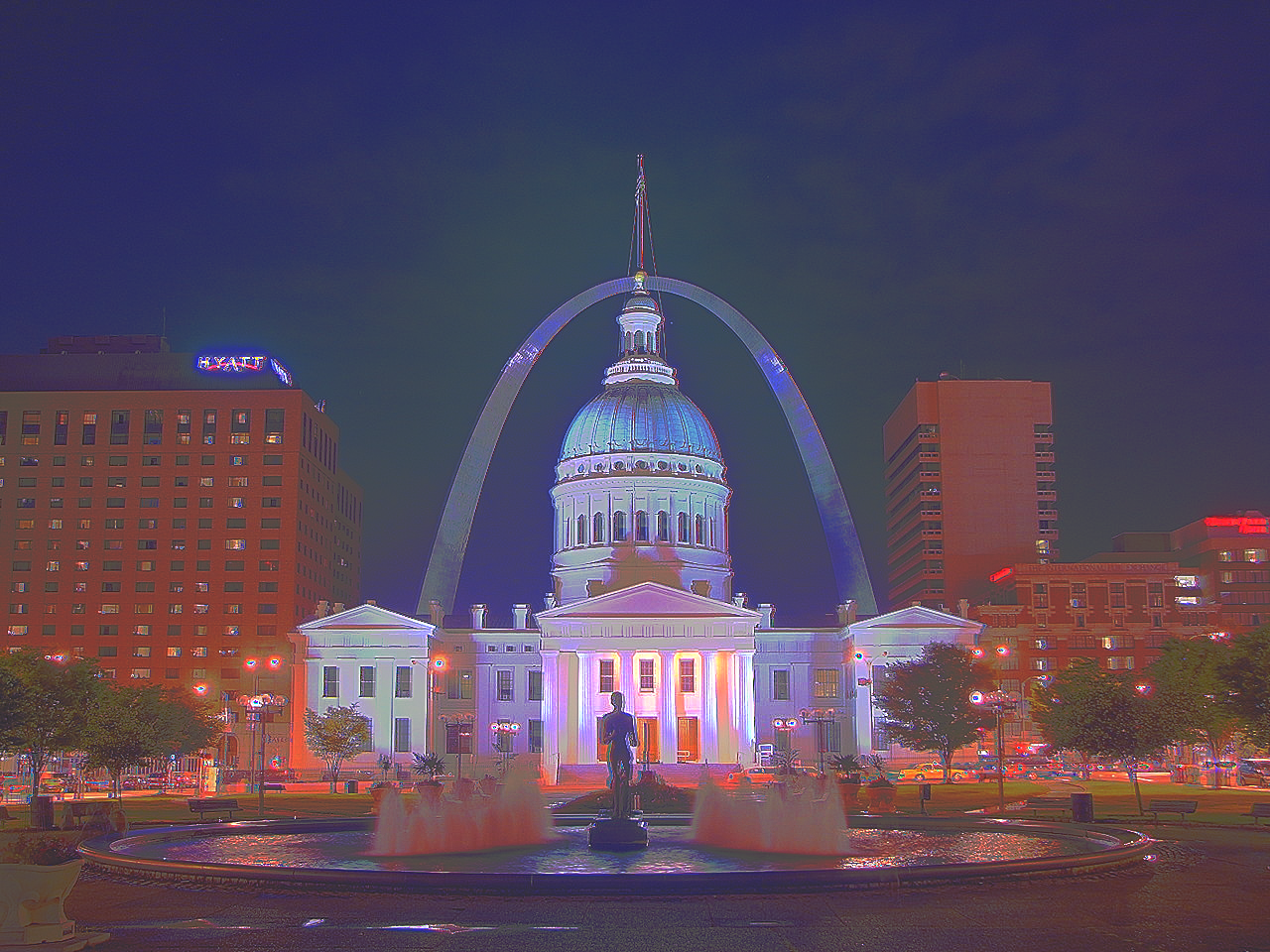

Durand Local

Global Simple
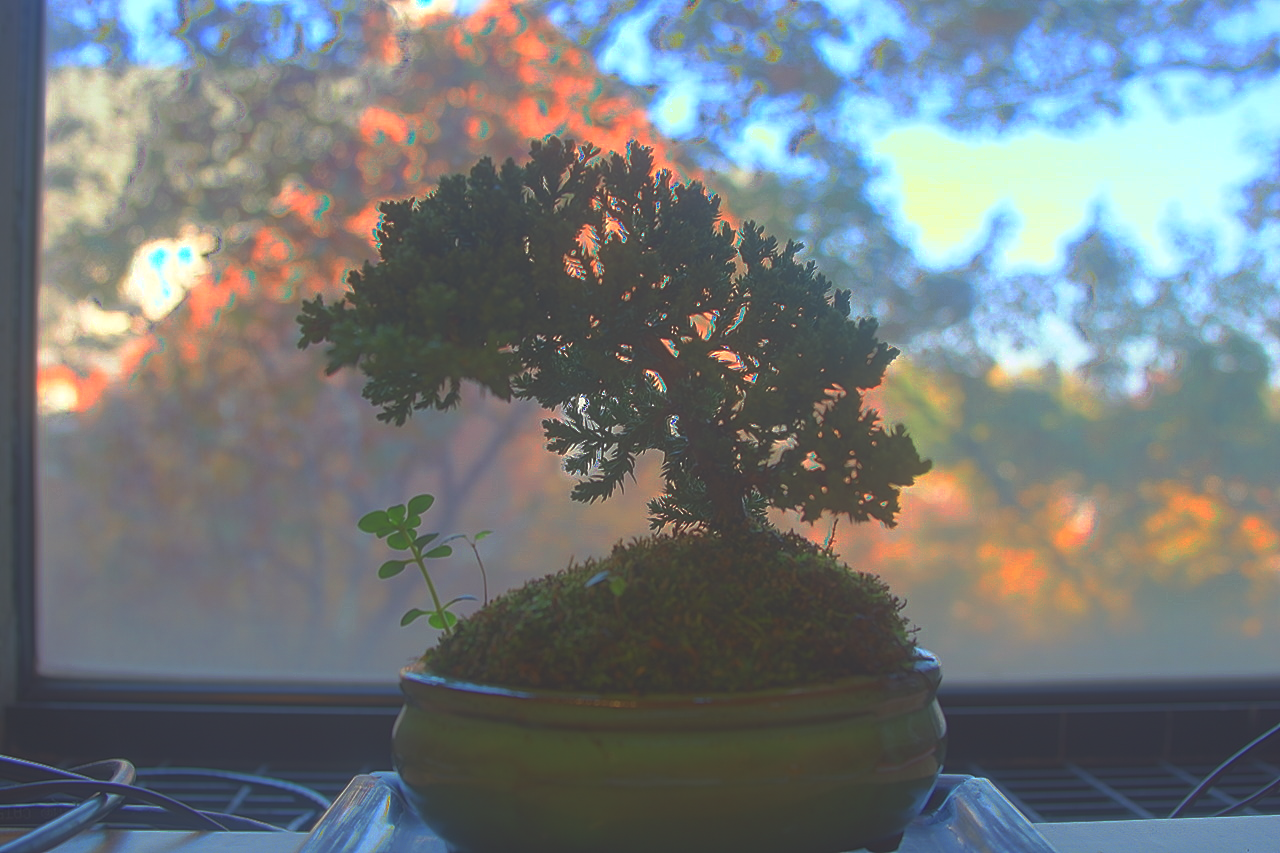 Durand
Durand
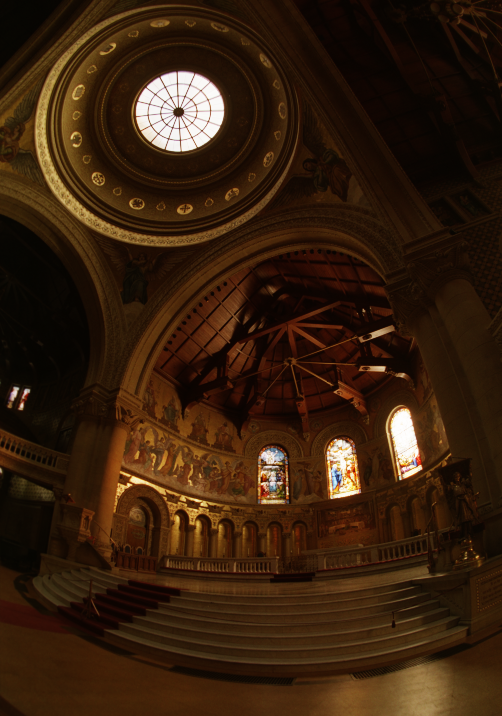

Global Simple
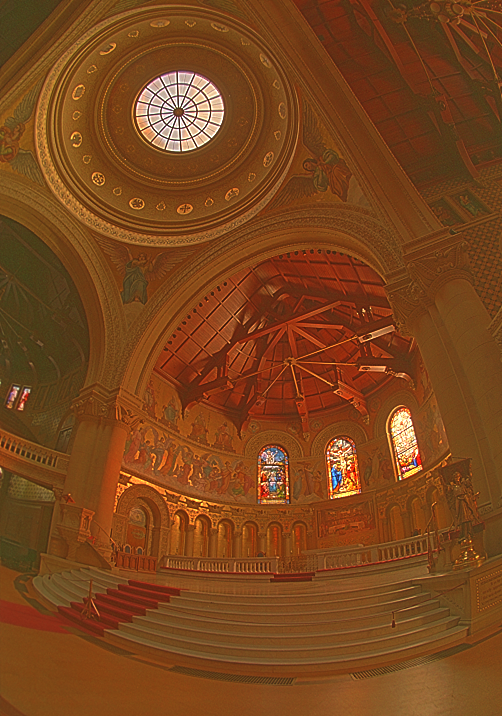

Durand
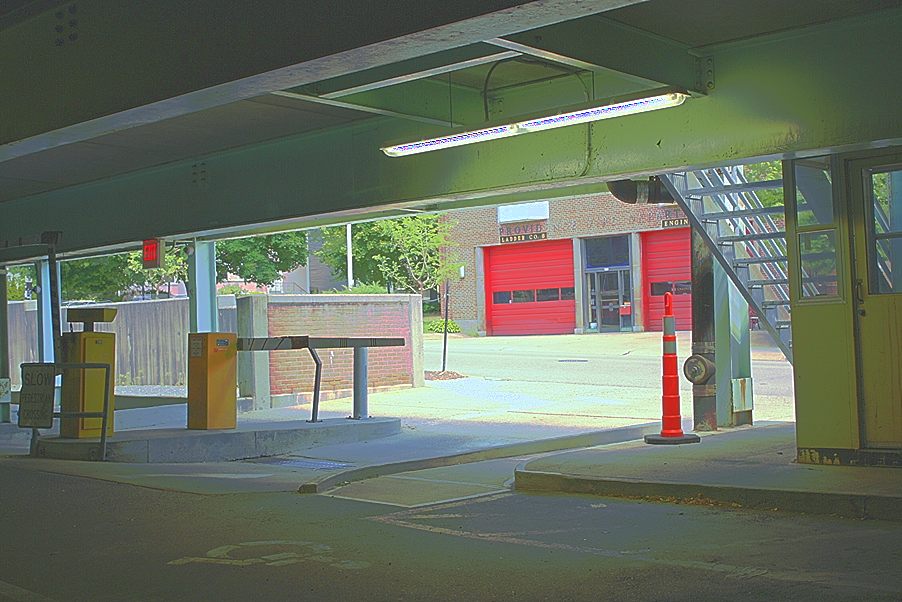

Garage
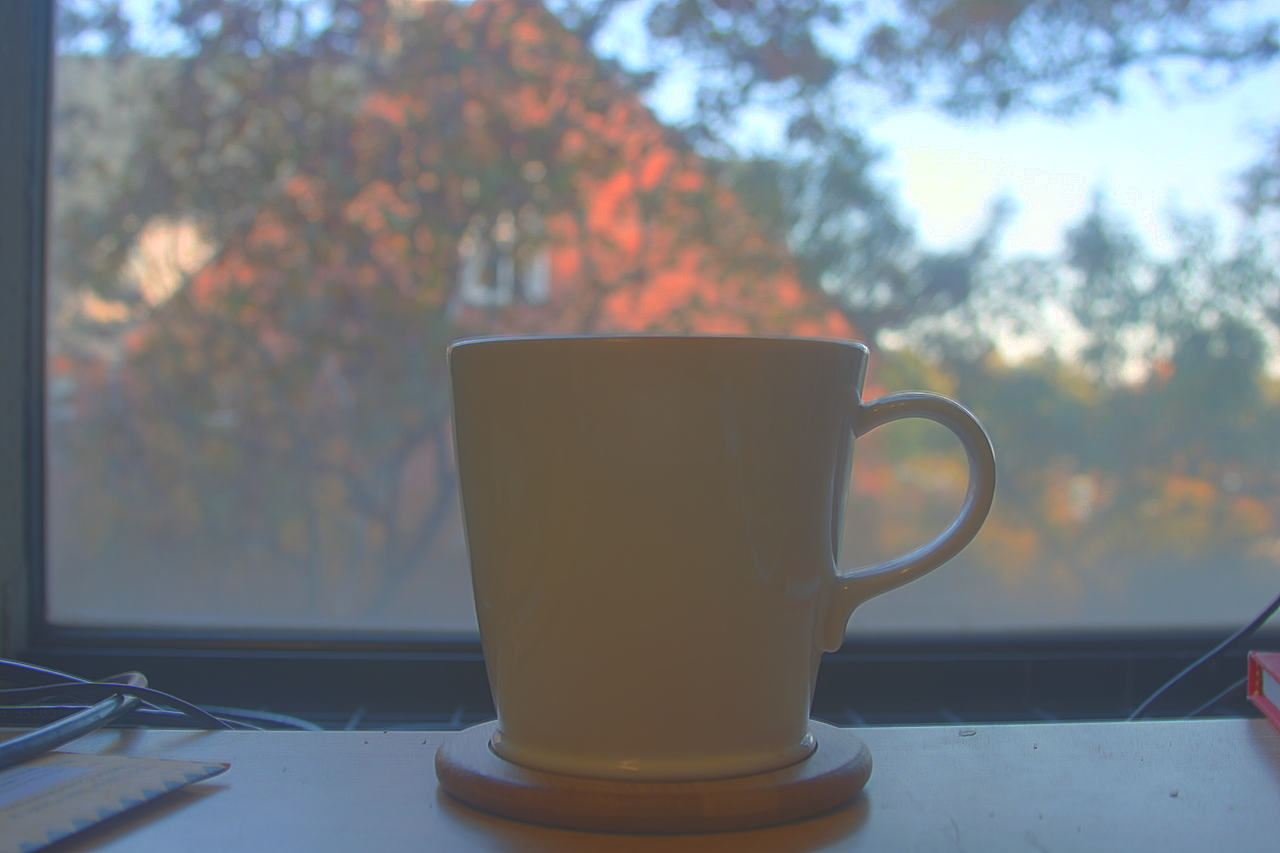

Mug
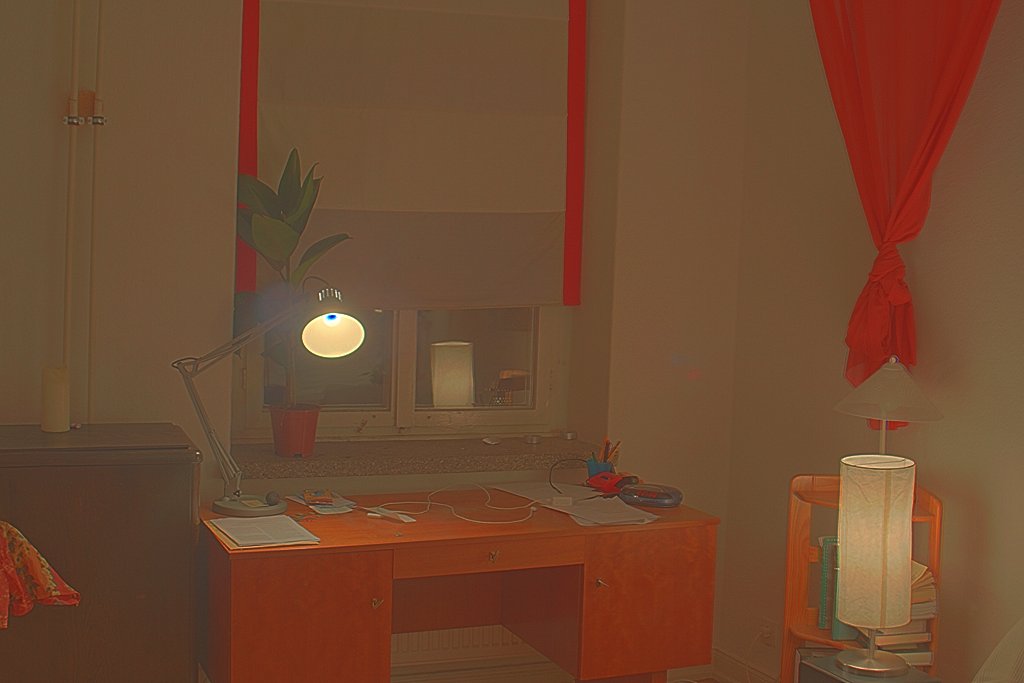

Window
However, some of the LDR exposures are unaligned, and lead to poor results without aligning them. However, aligning can be a challenge becuase the images are taken at different exposures and have very different lighting. I used OpenCV's find Enhanced Correlation Coefficient method to generate a perspective warp for each image from the middle exposure.
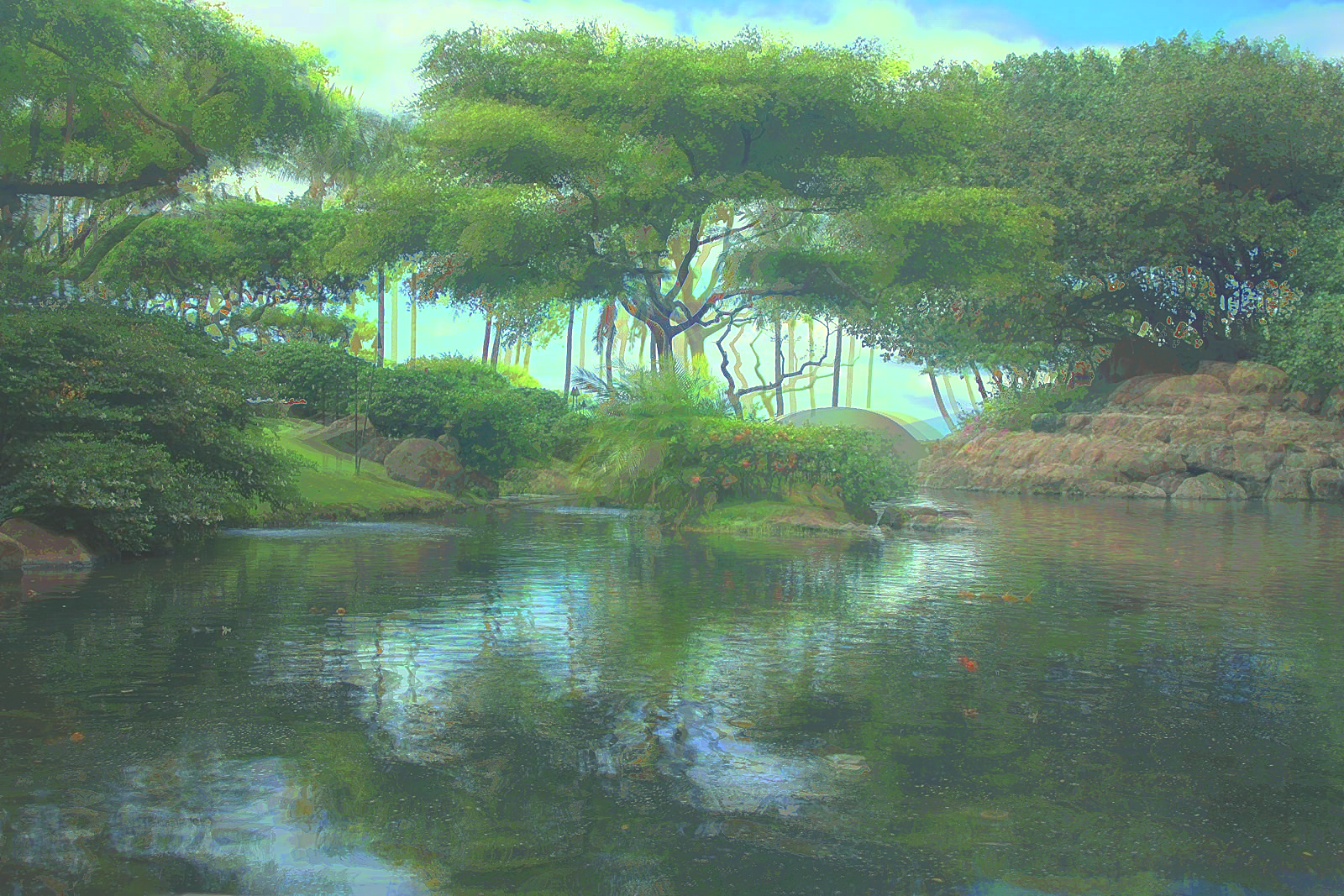

No Alignment
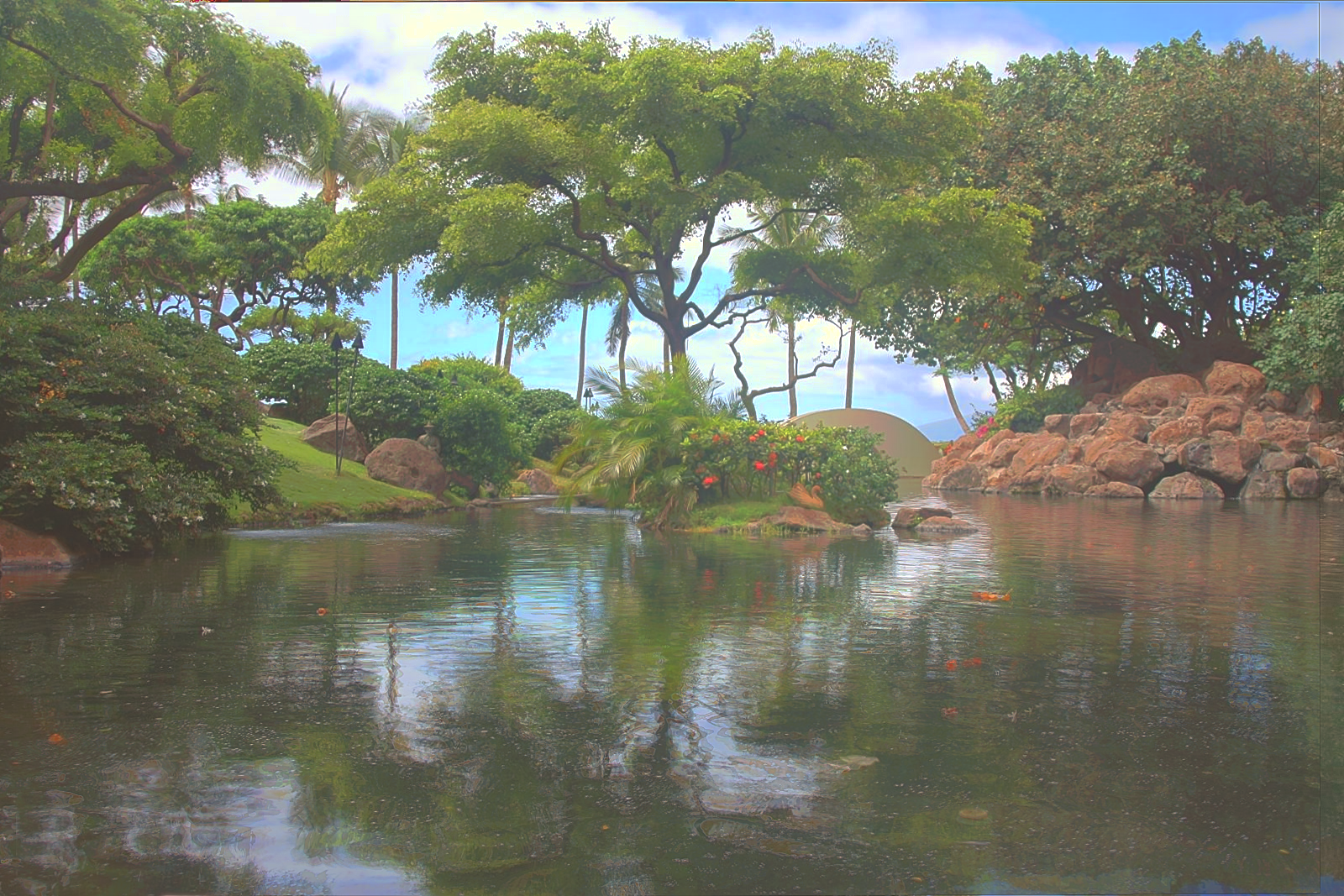

Alignment

No Alignment

Alignment